How to Protect Backups From Ransomware? 5 Proven Practices
Your data is only as safe as its backup. Hackers and mal-actors are increasingly targeting backups as the recent Uber breach highlights. In fact, the US Cybersecurity Agency, CISA, added flaws that specifically affect certain backup solutions to its Vulnerability Catalog . Your backups are what you’ll turn to when you need to restore your data and ensure business continuity in the event of a malware or ransomware attack. But what if your backups themselves are infected? It could be devastating for your business. How can companies protect backups from ransomware? Here are 5 proven best practices for securing your backups from ransomware.
#1 Ensure Cyber-Resiliency of Backups
The first step to protect your backups from ransomware is to ensure their cyber-resiliency. Keeping your backups immutable, air-gapped, and will keep them cyber-resilient in the event of ransomware attacks.
Keep your Backup Data Immutable
To guarantee the data integrity of your backups check that they are immutable. Ransomware will not able to modify or encrypt the backup data if the backups are immutable. Consider object-based storage such as Amazon S3 or Azure Blob Storage. Immutability is essential to protect backups from ransomware.
Air-gap Sensitive Data
For more sensitive data, keep the backups securely within an air-gapped storage container. Some options include which offers WORM techniques (Write Once, Read Many) and “Object locking” capabilities. Backups that are not connected to the internet or a network in any way are called air-gapped backups. Data kept this way is much more secure from infiltrating ransomware, as well as other bad actors who might attempt to disrupt it. In the past, people used tape media to store their backup data offline in a physical location. However, since backup has evolved, using a cloud-based destination is now your best option.
Implement Redundancy with the 3-2-1 Rule
Data redundancy is a simple but necessary part to ensure backup data survivability. The 3-2-1 backup rule is an industry best practice. It recommends having three copies of their data with two stored in different formats, with one being stored offsite. This ensures data redundancy in case data is corrupted or destroyed by a breach or cyberattack. Implementing redundancy per the 3-2-1 rule will help businesses make sure they have multiple copies of their data saved in different locations, providing improved security and reducing the risk of data loss.
#2 Use Strong Encryption For All Backups
Encryption is a crucial part of protecting backups from ransomware. Utilizing strong encryption protocols ensures that only authorized persons have access to critical data, giving you peace of mind that your backup data is safe. We recommend encrypting data at every stage of its life cycle, including when it is at rest and in transit. Check that all third-party apps that process your data, including your backup solution, encrypt the backup data both in transit and at rest. Industry gold standards include SSL/TLS in-transit encryption and AES-256-bit encryption for data at rest.
#3 Secure Access with the Zero Trust Model
In recent years, the Zero Trust Model has become one of the most popular and effective ways to secure access. This model no longer trusts any entity/app within an organization’s infrastructure and requires verification or authentication of users both inside and outside the network.
- Check that your backup solution supports the Single Authentication Markup Language (SAML) with Okta, Open Authorization (OAuth), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), to ensure only authorized users are able to access data and applications at any given time.
- Implement ‘least privilege’ access to the backup service. Prevent unauthorized access by restricting backup/restore requests to company-approved IP addresses. IP “allowlisting” is particularly helpful for the workplaces of today with distributed/hybrid employees.
- Additionally, check that the backup solution is PCI-compliant with robust in-app security practices such as secure SDLC, intrusion detection, secure backup storage servers, and compliance certifications.
- Lastly, don’t forget to enforce a strong password policy.
All this combined makes sure access is granted only when due diligence is taken for true user identity confirmation in order for firms to increase their security posture. Thus protecting your backups from ransomware.
#4 Train your Employees on Cybersecurity Best Practices
CISA recommends that ransomware awareness training should be included in regular employee cybersecurity education. Training your employees about ransomware can significantly mitigate the risk of ransomware as phishing is the most common vector for ransomware. Some ransomware training tips:
- It’s important to train your employees on how to spot and report suspicious emails. Emphasize the red flags in terms of generic salutations, poor content grammar and spelling, unusual/non-official sender email addresses, and urgent requests for personal information
- CISA recommends ransomware awareness training, Training Employees About Ransomware Can Mitigate Cyber Risk, phishing is the most common vector of ransomware, Train employees on how to spot and report suspicious emails, what to include in the training: ransomware basics, spotting phishing red flags, and precautions when using flash media, lastly develop a Ransomware Incident Response Plan that is communicated across your company.
- It is also important to outline digital hygiene best practices such as being judicious with clicking on links in emails, especially shortened ones, not opening attachments unless they have been scanned, avoiding flash media, and only installing software and apps in your company’s “allowlist”.
- Lastly, companies should develop a Ransomware Incident Response Plan to ensure that everyone understands their roles if an incident does occur.
#5 Test Your Backup and Recovery Process Regularly
You should test your backup and recovery processes regularly to ensure that they are working as expected and that you can actually recover your data in the event of an attack. There are two main types of tests: Full system restore, which restores your entire system from scratch including the operating system, applications, and data; and partial file restore, which only restores a small subset of files or data. Conduct tests at least monthly, or more frequently if you have a high volume of changes to your system. Here are some helpful Whys and Hows of Backup and Recovery Testing. A robustly tested backup and recovery process also help with smooth data recovery, lower downtime, and Recovery Time Objective – all of which leads to seamless business continuity and quick recovery from ransomware.
Ransomware Proof Your Backups With CloudAlly
CloudAlly takes a holistic and ransomware-resistant approach to backup, which includes all of the best practices discussed in this blog post.
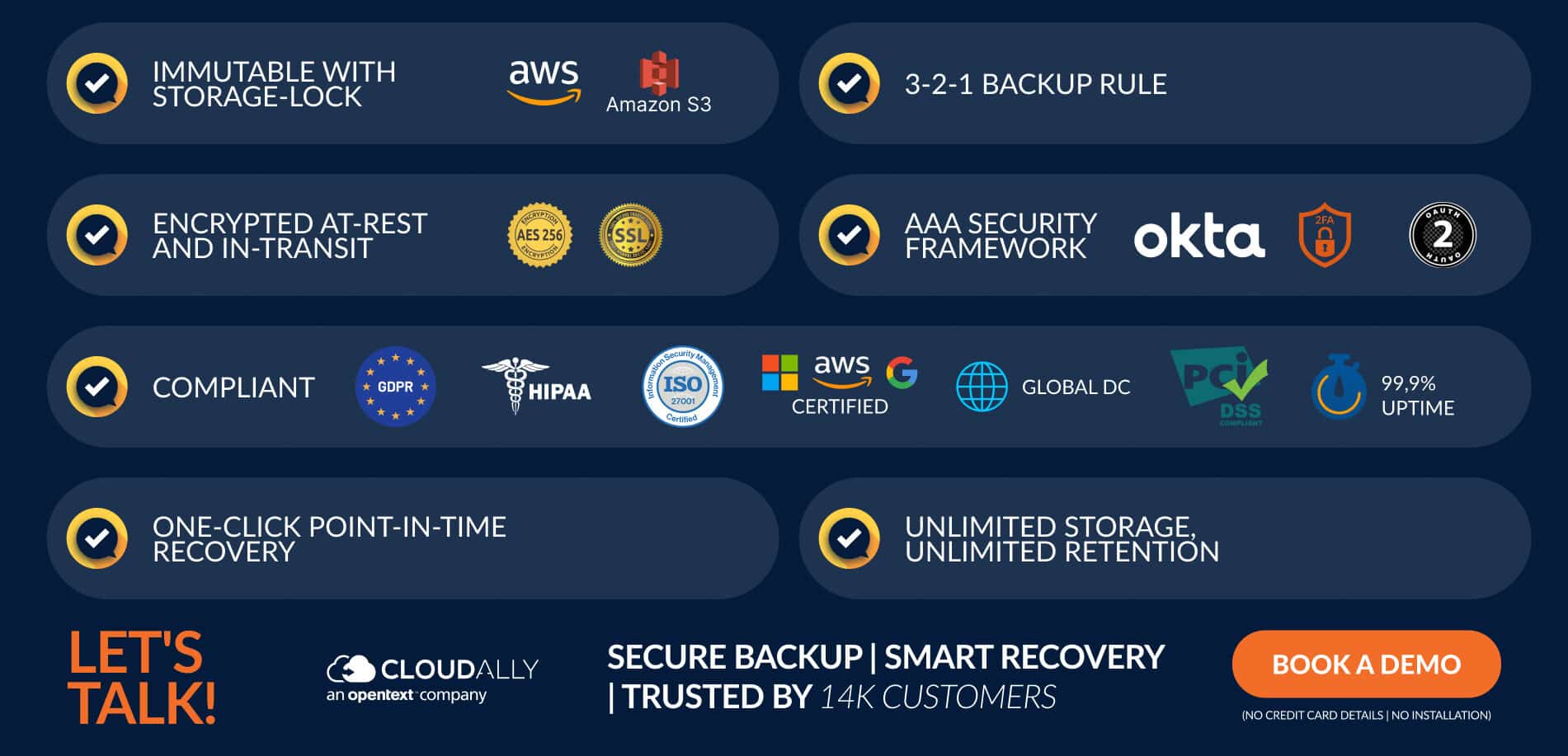
How does CloudAlly Protect Your Backups From Ransomware?
- All of CloudAlly’s data is kept in Amazon S3 immutable storage and encrypted using strong AES-256 bit encryption methods, with protection via SSL (HTTPS) enabled servers that are well hardened and up to date with the latest security updates.
- We also provide data backup with S3 Object Lock for sensitive data to meet stringent data regulations.
- CloudAlly keeps one copy on Amazon S3 and another copy on Glacier for full data redundancy to conform to the 3-2-1 rule.
- All our backups come with unlimited storage and unlimited retention for unlimited point-in-time recovery, allowing users to seamlessly restore their data from any point in time.
- Essentially, CloudAlly offers comprehensive multi-SaaS backup and recovery with one intuitive tool. Protect all your SaaS data – Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox, and Box.
Watch how CloudAlly’s ransomware recovery “saved the day” for one of Canada’s fastest-growing service providers.



